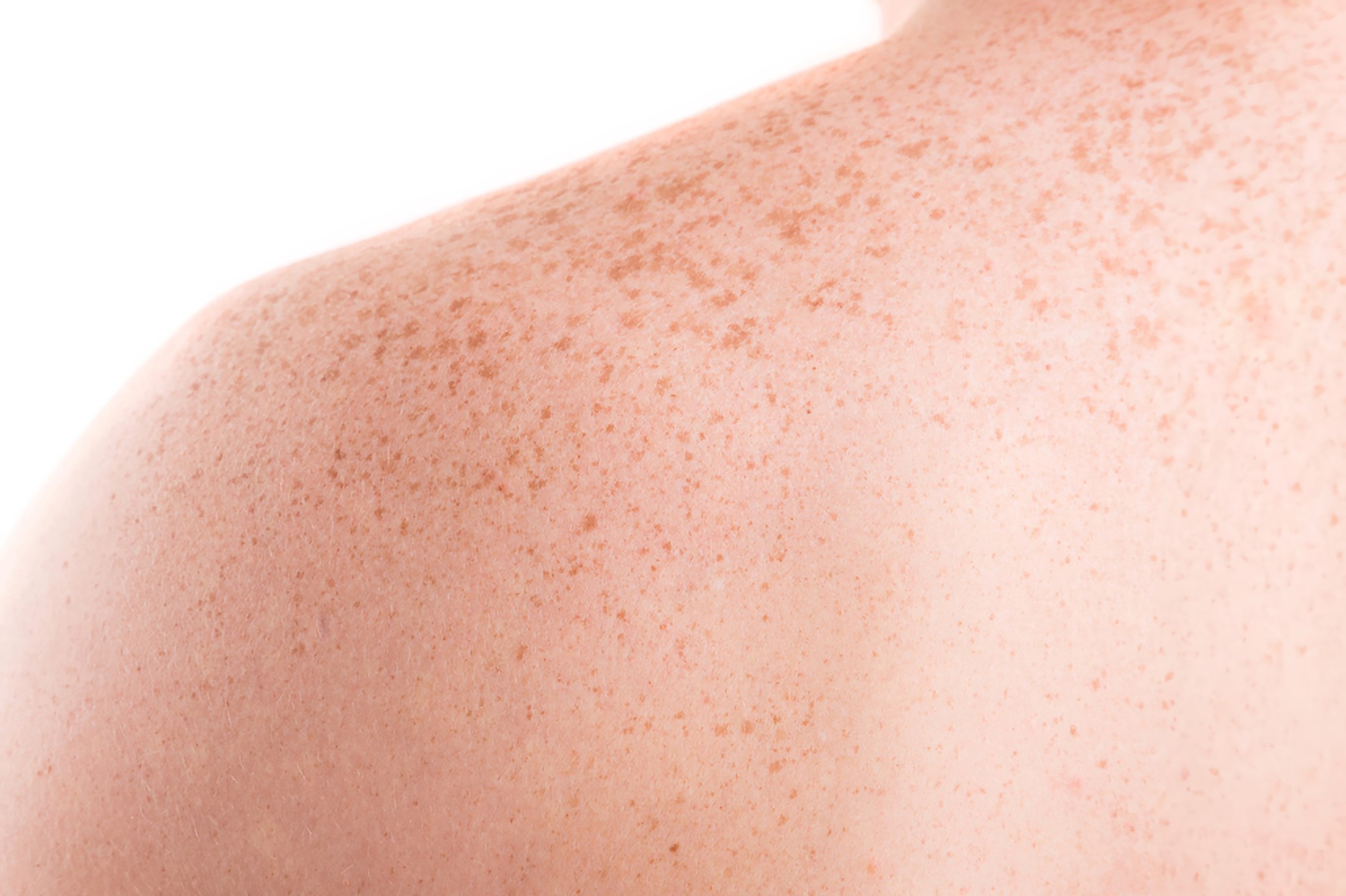
Skin pigmentation disorders have become a common occurrence in the world today. Conditions such as post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation, melasma, vitiligo, and erythema refer to these issues. They vary in severity; some individuals experience severe skin pigmentation, while others encounter milder forms. Each form is unique with its own characteristics. Understanding the symptoms and nature of each skin pigmentation disorder is essential to develop suitable treatments and preventative solutions.
In Singapore, pigmentation laser treatment has emerged as a preferred method for addressing skin pigmentation issues. Laser therapy can effectively reduce melanin in the skin, leading to a more even complexion. Advanced laser technologies are now capable of targeting deeper pigmentation without causing irritation or damage to the skin. This makes laser treatment a viable option for those seeking solutions to pigmentation concerns in Singapore.
Four Categories of Skin Pigmentation Disorders
Generalised Hyperpigmentation
Generalised hyperpigmentation is a form of skin pigmentation disorder characterised by excessive skin pigment production all over the body. Individuals with this disorder often have a bronze tinge to their skin caused by the excessive production of the melanocyte-stimulating hormone.
Common conditions associated with generalised hyperpigmentation include Addison’s disease, hemochromatosis, metastatic melanoma, and exposure to afamelanotide.
Localised Hyperpigmentation
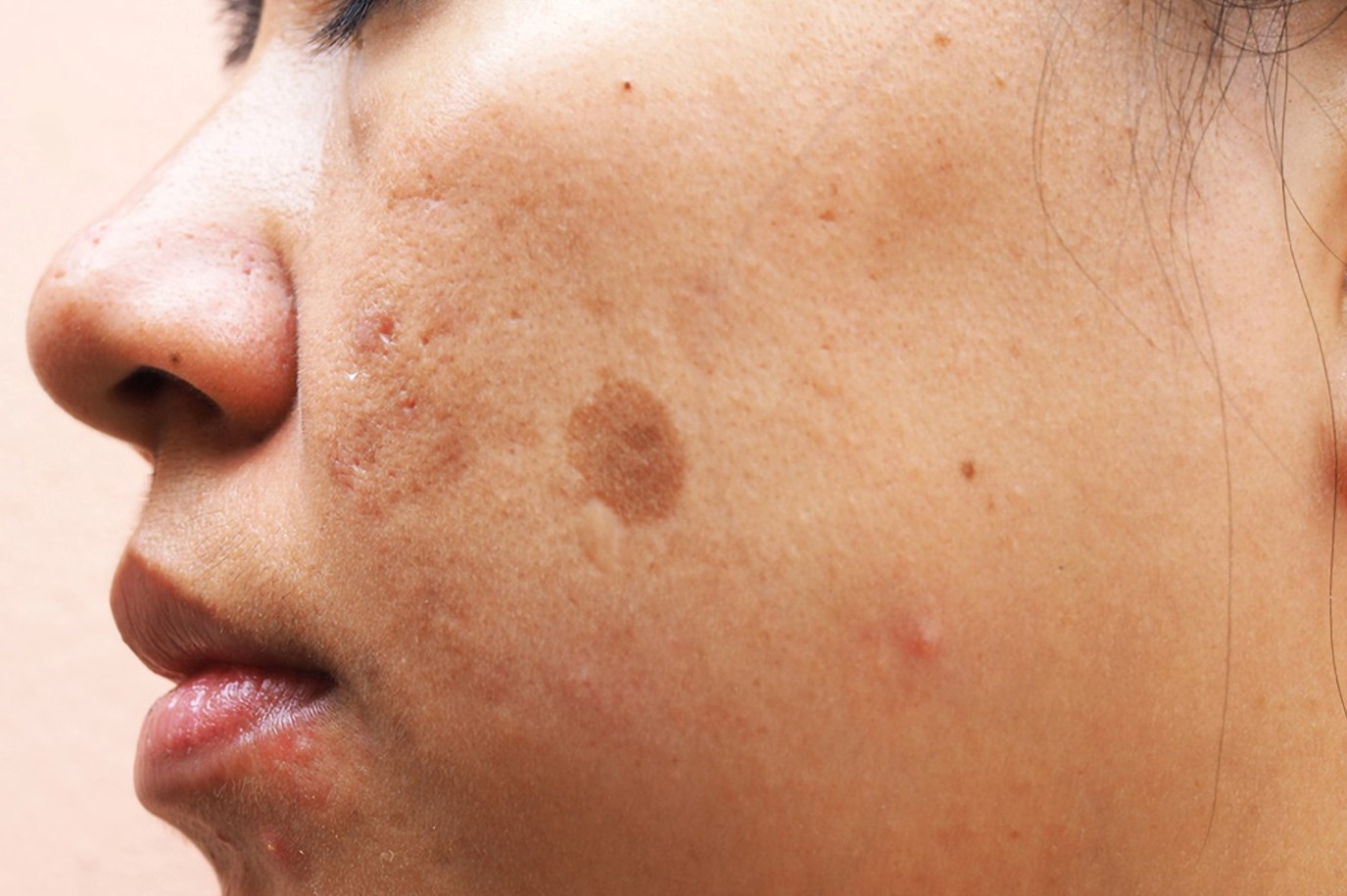
Unlike generalised hyperpigmentation, localised hyperpigmentation involves the production of excessive pigments in certain localised areas of the body. These pigments may include Melanin, hemosiderin, or any other external pigment. Skin lesions may cause localised hyperpigmentation. These may include moles and seborrheic keratosis. An inflammatory skin condition like eczema or skin cancers like melanoma and basal cell carcinoma may also cause it. Other causes of localised hyperpigmentation may include thickening of the skin caused by acanthosis nigricans, internal bleeding leading to pigmented purpura, accidental tattoos, and infection of the skin.
Generalised Hypopigmentation
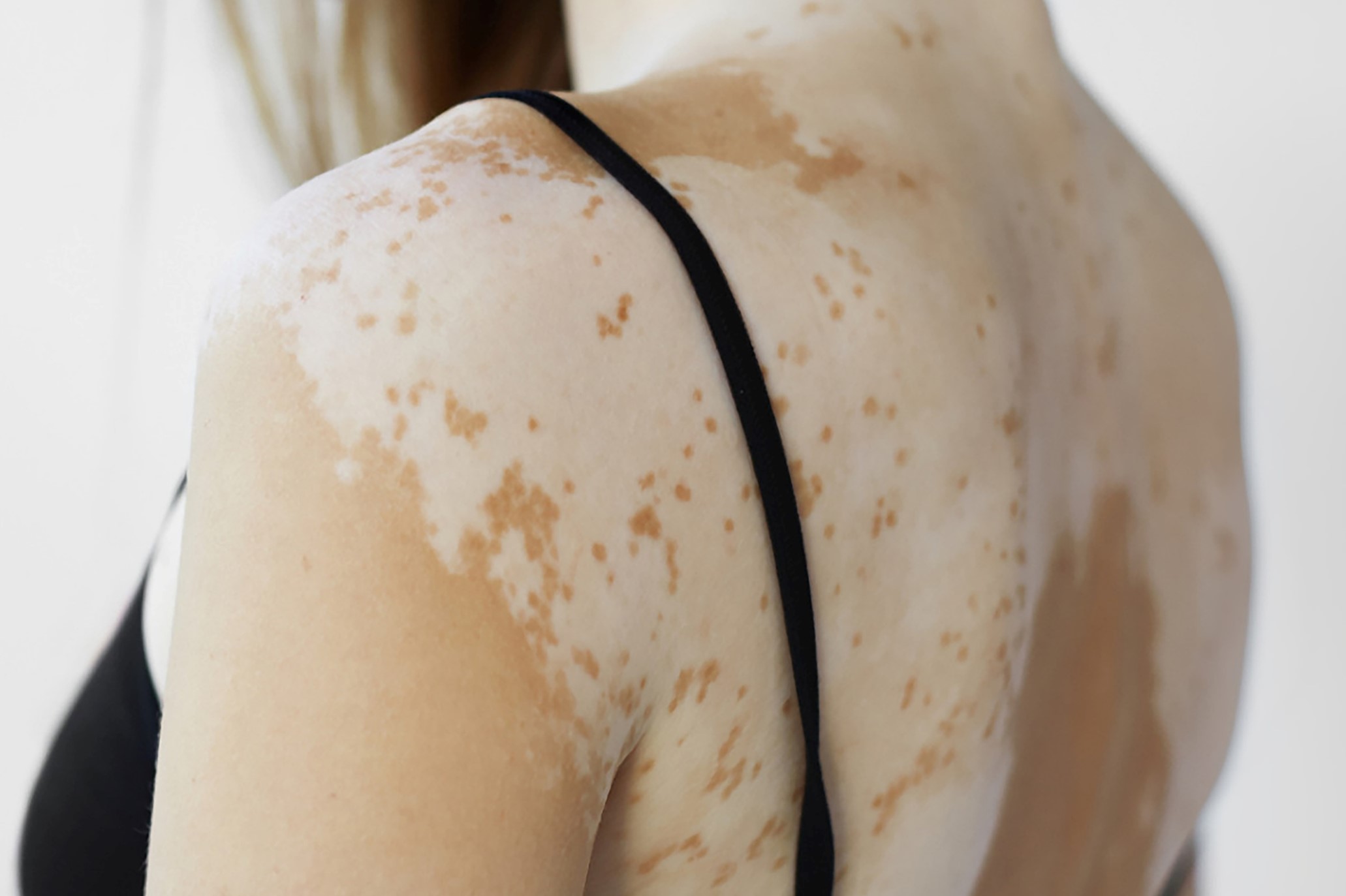
Hypopigmentation is a condition that is characterised by a reduction in skin pigmentation. This happens when there is lesser production of skin pigment all over the body. It may be congenital in nature, which means it has been present since birth, or it may be due to autoimmune conditions like Albinism. A pituitary gland failure may also cause generalised pigmentation. Since the pituitary gland produces the melanin-stimulating hormone, a lack of this hormone in the body due to pituitary failure may lead to a generalised melanin reduction.
Localised Hypopigmentation
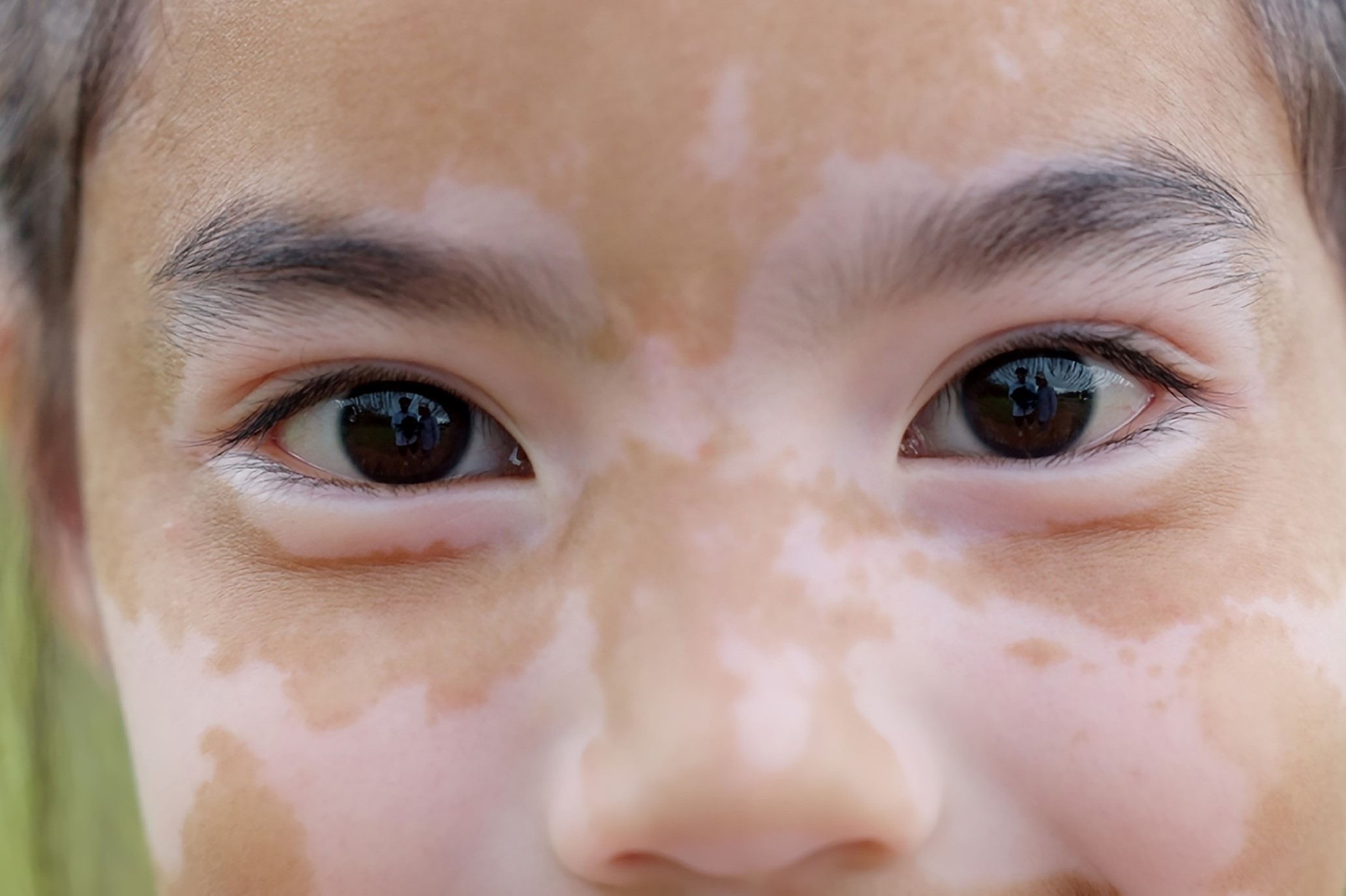

Localised hypopigmentation is a skin pigmentation disorder where there is a reduced amount of pigmentation in localised areas of the body. Localised hypopigmentation may also be associated with vascular changes. Some individuals may have this condition since birth, referred to as congenital localised hypopigmentation. The others may acquire it over time from certain environmental changes or health conditions. Common conditions that might promote localised hypopigmentation disorders include Pityriasis alba, Leprosy, Syphilis, and macular hypomelanosis.
Treatment for Hyperpigmentation
If an area of the body is affected by excess production of Melanin, the individual may opt for lightening skin creams. These commonly include topical retinoids, azelaic acids, topical corticosteroids, hydroquinones, glycolic acids, and vitamin c serums. The individual may also opt for treatments like chemical peels, IPL treatment, lasers, and dermabrasions conducted under an experienced practitioner.
Treatment for Hypopigmentation
Skin pigmentation disorders characterised by general and localised hypopigmentation may resolve on their own over time. This may take several weeks to months after the causation factors have been resolved. However, certain hypopigmentation disorders like Vitiligo and achromia may not be treated on their own, and the results of therapies are also highly variable.
What Are the Different Types of Skin Pigmentation Disorders?
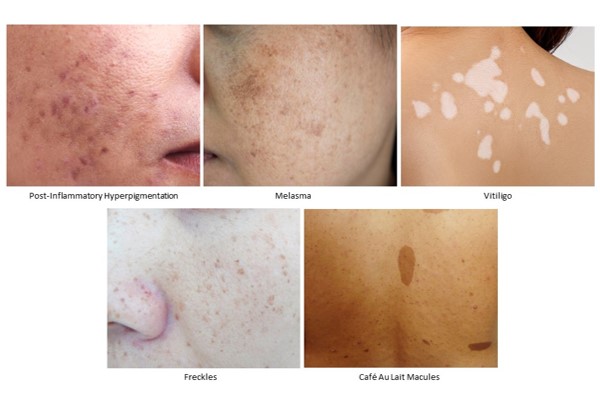
Post-Inflammatory Hyperpigmentation
Hyperpigmentation after skin damage or an inflammatory condition of the skin is a common type of skin pigmentation disorder. This may be common in individuals who have had previous skin infections, burns, blisters, or other forms of trauma to their skin.
Vitiligo
Vitiligo is a form of hypopigmentation, where the individual may present with loss of skin colour. This loss of pigmentation in the skin is most commonly seen in patches. While the patches may be smaller in size at the beginning, they begin to grow over time. Vitiligo may be present on the skin overlying any part of the body. It may also affect the hair and the inside of our mouth.
Melasma
Melasma is essential for managing this skin pigmentation disorder, which causes patches or spots on the face that are darker than the individual’s skin tone. As a form of localized hyperpigmentation, melasma treatment aims to reduce these darkened areas effectively. Given that melasma can be mistaken for other skin conditions, consulting an experienced practitioner is crucial for an accurate diagnosis and developing an effective melasma treatment plan.
Freckles (Ephelides and Lentigines)
Freckles, which may also be referred to as Ephelides and Lentigines, are a form of skin pigmentation disorder. Freckles are present as small spots on the skin, which range in colour from red to dark brown. They are usually present in the area of the skin most exposed to the sun, which may include the face, neck, upper chest, neck, hands, and arms. The primary difference between ephelis and lentigines is that while ephelis fades during the winter season, the lentigines remain, even without sun exposure.
Autoimmune Conditions
Other autoimmune conditions which may lead to skin pigmentation disorders include Lupus Erythematosus. Lupus Erythematosus commonly affects the skin and causes excessive photosensitivity. This photosensitivity, in turn, leads to hyperpigmentation.
Café Au Lait Macules
Café au lait macules are well-circumscribed pigmented patches or macules found on the skin. The colour of these macules may range from light brown to dark brown. The size of these macules also ranges from a few millimetres up to 200 millimetres. Café au lait macules are usually harmless for individuals; however, having more than 6 spots of freckles on the groin or the underarm area may be indicative of a condition known as neurofibromatosis type 1.
Pigmentation Disorders Caused By Genetics
Genetics may play an important role in skin pigmentation disorders, especially localised forms of hyperpigmentation. This may be commonly seen in birthmarks, port wine stains, and haemangioma.
What Are The Causes Of Skin Pigmentation Disorders?
Skin pigmentation disorders, whether localised or generalized, may be caused by a number of factors. However, the pigment which is most commonly involved in these disorders is Melanin. Increased production of Melanin can lead to hyperpigmentation, while reduced melanin production leads to hypopigmentation. The primary causative factors which are involved in skin hyperpigmentation include acne, pregnancy, and sun damage.
Acne
An acne breakout is another common cause of skin pigmentation. Acne can cause excessive skin scarring and is associated with discolouration of the skin. The pigmentation caused by acne is often referred to as post-inflammatory discolouration, which is associated with increased melanin production around the area of acne scarring.
Pregnancy
Hormonal changes during pregnancy are another common cause of abnormal skin pigmentation. The changes in hormone levels can lead to an increase in the Melanin producing cells in the body. This results in the formation of dark spots, also known as Melasma. This is so common that Melasma is also referred to as the mask of pregnancy.
Sun/Ultra Violet Damage
Exposure to the sun’s ultraviolet radiation can cause excessive and uneven production of skin pigmentation over time. This can cause the appearance of dark spots and patches on sun-exposed skin surfaces. Hence, it is very important to always use sunblock before going outdoors.
Diagnosis and Tests
In order to diagnose skin disorders, the doctor may conduct a number of tests and examinations. This allows the doctor to make an accurate diagnosis in order to come up with a suitable solution. Some other diagnostic methods which may be conducted include:
- Woods Lamp Examination: Woods lamp examination involves using a long wave ultraviolet light, which is directed at the area with the skin pigmentation disorder. The skin pigmentation disorders which may be diagnosed through this method like hypopigmentation, hyperpigmentation, and other colour-changing lesions and blemishes.
- Skin Biopsy: Skin biopsy may also be used as a diagnostic method for skin pigmentation disorders. It involves the extraction of tissue samples from pigmented areas. These extracted samples are then examined to identify the type of pigmentation disorders which is present.
Treatments For Skin Pigmentation Disorders
Hydroquinone
Hydroquinone often opts as a form of treatment for hyperpigmentation of the skin. It is often used for Melasma and hyperpigmentation by many experts. When hydroquinone is used topically for the management of hyperpigmentation, it is considered safe and is not associated with any long-term side effects.
Retinoids

Retinoids may also be used for the treatment of pigmentation disorders. Retinoids work by reducing the amount of Melanin found in the skin layers. It does this by blocking the action of the enzyme responsible for melanin production. It is important to start using retinoids according to the doctor’s recommendation, as inappropriate use may lead to skin inflammation.
Azelaic Acid
Azelaic acid may also be used as an effective treatment for the treatment of dark spots, Melasma, and other skin pigmentation disorders. It works by inhibiting the action of the tyrosinase enzyme – which is responsible for producing skin pigment. The concentration of Azelaic acid, which is found to be particularly effective for this, is between 15 to 20%.
Chemical Peels and Lasers
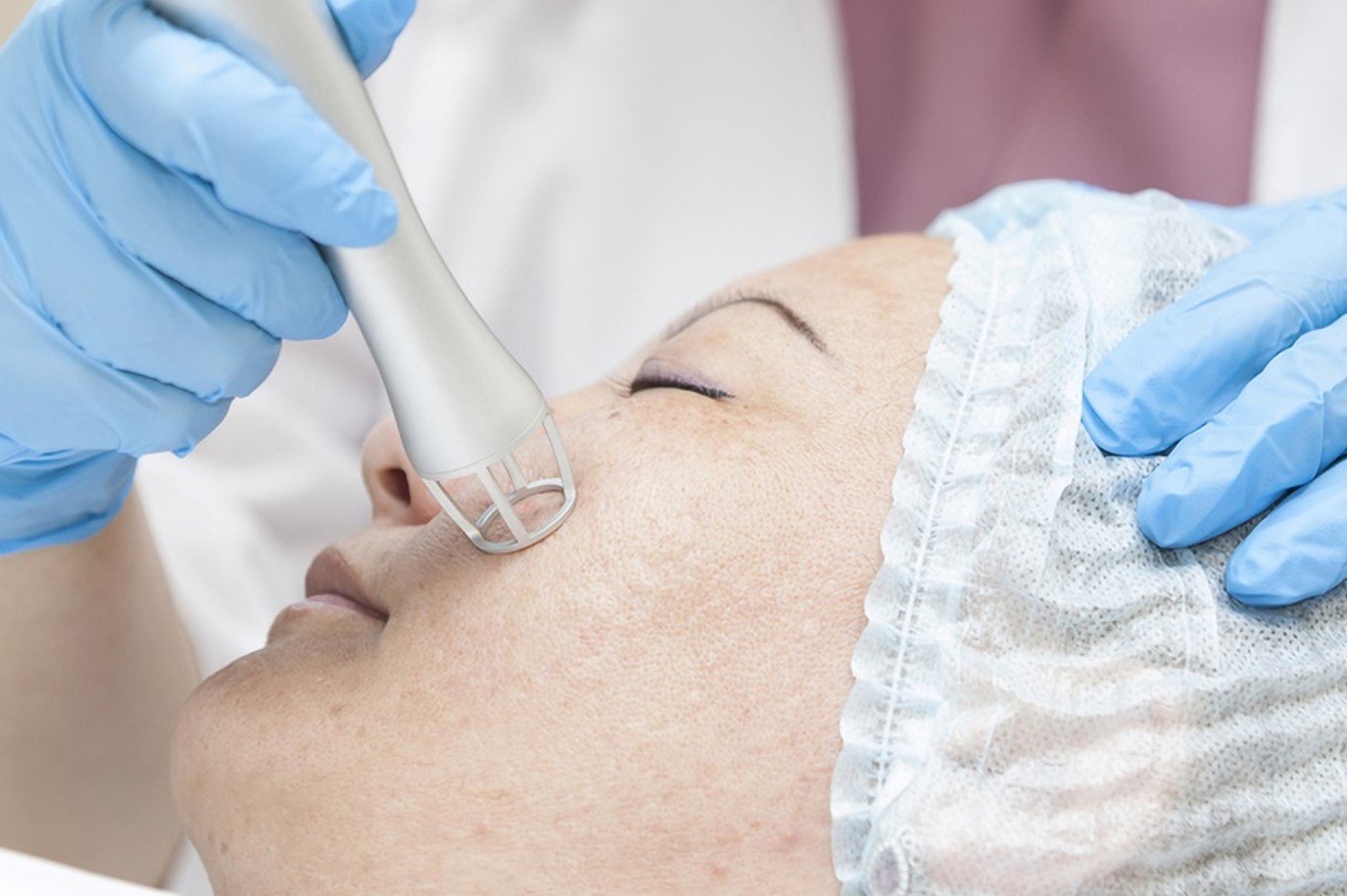
Chemical peels and lasers are also used for the reduction of skin hyperpigmentation. Chemical peels involve the application of acids like glycolic or salicylic acids to the skin surface, which help target remove the top layer of skin and target discolouration. Similarly, laser works by targeting skin pigmentation by directly acting on the skin pigment cells and destroying them.
UV Light Therapy
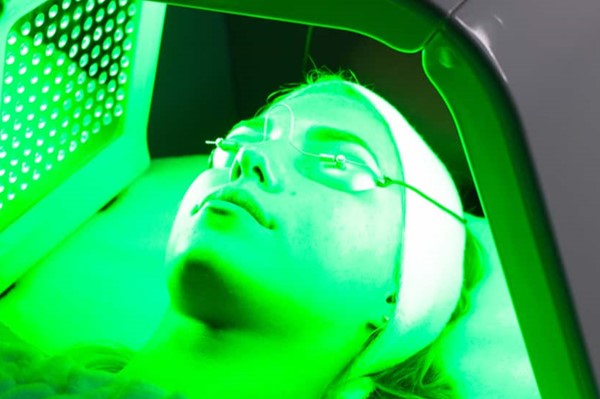
UV light therapy is another effective way to target skin pigmentation. It is considered much safer compared to the more invasive alternatives. UV light therapy may include blue and red light therapy. While blue light therapy targets excessive pigmentation, red light therapy boosts collagen production.
Final Thoughts
The aesthetic physician or the dermatologist can help you identify your skin pigmentation disorder. An accurate diagnosis is key to an effective cure; hence, it is essential to choose an experienced and certified doctor for the treatment of your skin pigmentation.
About Dream Aesthetics and Plastic Surgery
Bespoke surgical for cosmetic or medical reasons is what Dream covers to bring out the beauty in every individual. Going beyond the aesthetics and working on physical anomalies are what we value the most in leading our patients to cherish self-improvement and confident lifestyles.
Derived from Associate Professor Vincent Yeow’s long-standing experience performing plastic surgery in Singapore, our treatment plans deliver physical remodelling in our patients’ favour. One of the notable remodellings is droopy eyelid correction. The ptosis surgery used for treatment eventually fixes drooping eyelids, improves vision and enhances appearance.
Most importantly, as a trustworthy plastic surgery and aesthetic clinic, we treasure positive and natural outcomes for each individual. We will ensure to deliver the beauty refinement of your dream without compromising your safety and privacy.