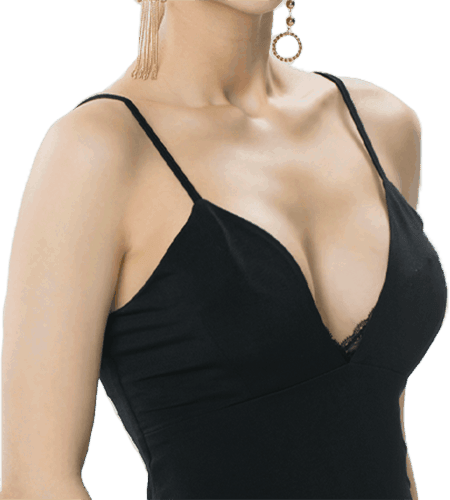

Breast Augmentation
For fuller, more natural looking breasts.
Procedure Time
2 Hours

Anaesthesia
General Anaesthesia

Recovery Period
10 – 14 Days

Stitch Removal
7 Days Post-op
What is Breast Augmentation?
Breast augmentation, also known as breast enlargement or breast implants surgery, is a cosmetic procedure to enhance the size, shape, and symmetry of the breasts. The procedure involves the placement of implants, which are typically made of silicone or saline, beneath the breast tissue or chest muscle to increase the volume and projection of the breasts.
The primary aim of the surgery for bust enhancement in Singapore is to change the shape or size of the breasts to make them look and feel better.
Breast Implant Profiles
In terms of breast enhancement, the profile of an implant indicates how fat breast implants extend from the chest surface. Breast implants are available in low, moderate, and high profiles.
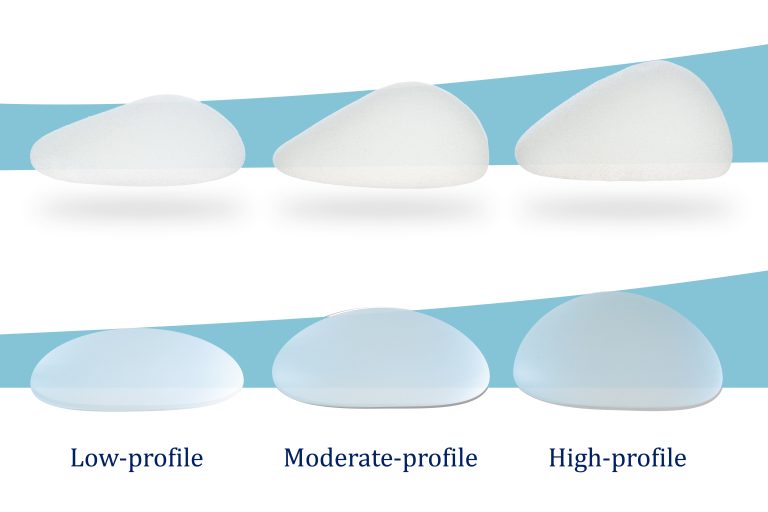

Low-profile implant
Provides the least projection and most subtle enhancement of breasts.
Moderate-profile implant
Ideal for achieving more volume and fullness in breasts.
High-profile implant
Provides breast enlargement by providing significant projection.
High-profile implants:
These implants have a narrow base and a high projection, which can create a more dramatic, “push-up” effect. They can be an option for women who want to achieve a more pronounced look, but may not be appropriate for women with a wider chest wall or a more natural-looking result.
Low-profile implants:
These implants have a wider base and a lower projection, which can create a more natural-looking result. They may be an option for women with a wider chest wall or those who want to achieve a more subtle increase in breast size.
Benefits of Breast Augmentation
- Enhance the breast appearance and fullness
- Expand inherently small-sized or underdeveloped breasts
- Reconstruct breast shape and contour
- Correction of breast asymmetry or unevenness
- Lifting drooping breasts
- Improvement in the overall stature
Incision Types Commonly Used in Breast Augmentation in Singapore
Incisions are hidden along natural crease lines or outlines or the areola to reduce visibility of scarring. We will discuss which incision options are appropriate for your desired outcome.
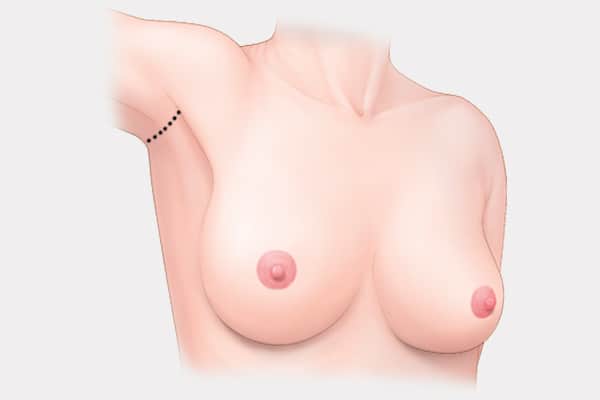
Armpit (Transaxillary) Incision
- Incision is made along armpit crease.
- No visible scar on the breast area.
- Enables breast-feeding after the surgery as it does not damage the mammary glandular tissue.
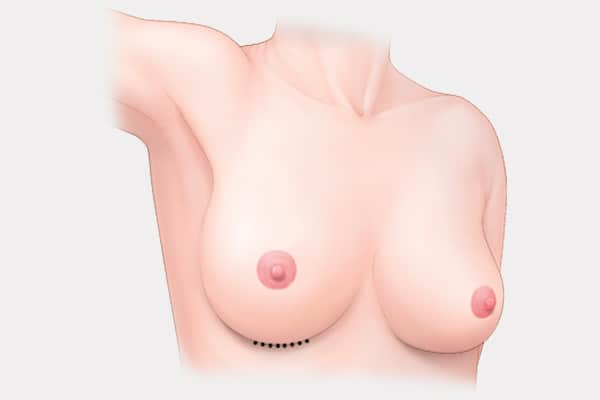
Breast Fold (Inframammary) Incision
- Incision made along the natural fold below breast.
- Most common incision method.
- Appropriate for inserting large implants.
- Recommended for revision cases who need major correction.
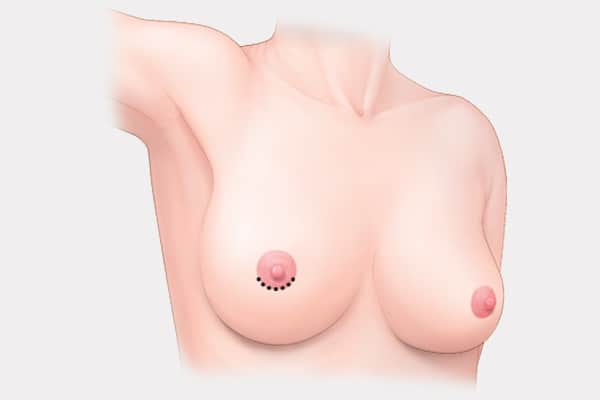
Areola (Periareola) Incision
- Incision made along line or the areola.
- Method can only be used if the diameter of the areola is 3.5cm or more.
- Scar is not obvious.
- Minimal pain compared to other methods.
- Easy to move arms after surgery.
- Nipple sensation after surgery may be affected.
Types of Breast Implants Shape for Breast Augmentation
Breast implants come in different shapes, and the choice of shape will depend on your individual anatomy and desired outcome.
Here are some of the most common types of breast augmentation:
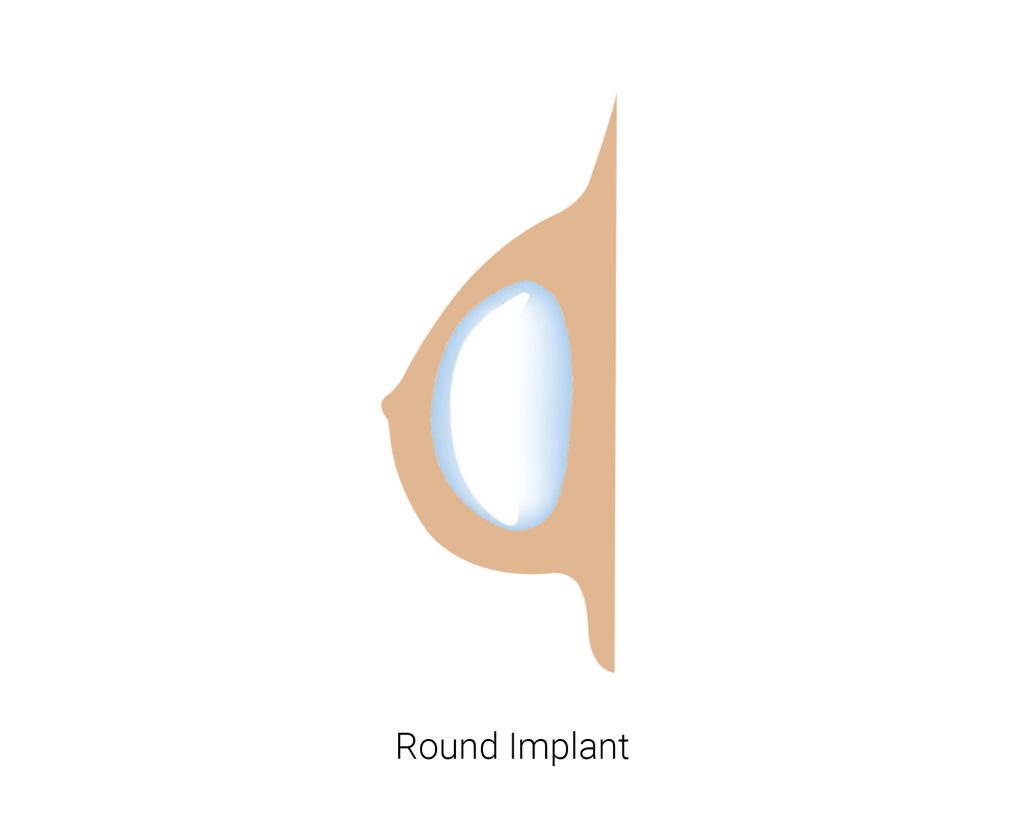
Round implants
These implants have a circular shape and are typically used to add fullness to the upper part of the breast. They can provide a more dramatic look and may be an option for women who want a more noticeable increase in breast size.
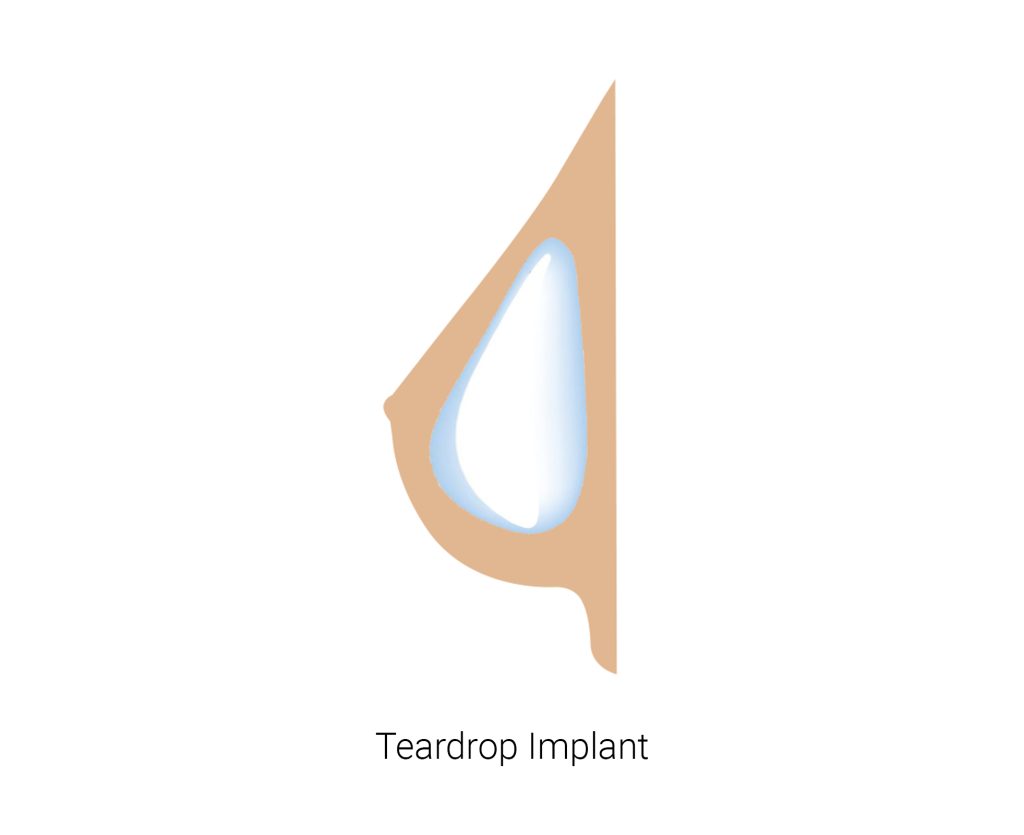
Teardrop or anatomical implants
These implants have a tapered shape that mimics the natural shape of the breast. They are typically used to create a more natural-looking result and may be an option for women who have little natural breast tissue or who want to achieve a more gradual transition between the implant and the natural breast tissue.
Breast augmentation can be a life-changing procedure for many women, but it’s important to carefully consider all the potential risks and benefits before making a decision. The choice of surgery approach, technique and implant shape will depend on a variety of factors, including your individual anatomy, the desired outcome, and your surgeon’s recommendations.
It’s important to carefully consider the potential risks and benefits of breast augmentation before making a decision and be sure to consult with a qualified and experienced plastic surgeon who can answer your questions and provide guidance on the suitable approach.
Types of Breast Implants in Singapore
Saline Implants
Saline breast implants are filled with sterile salt water. They have long been used for breast augmentation surgeries and are considered safer because even if an implant ruptures, the salt water will mostly be reabsorbed into the body. However, these implants have become obsolete, especially in Singapore, and are not a preferred choice. Instead, gummy bear implants, also known as form-stable implants, are used most commonly today.
Silicone Gel Implants
Silicone gel implants often give a more natural feel as they imitate the breast tissue. The newer silicone implants are called cohesive gel implants or form-stable implants. They are usually thicker and can keep the shape intact even if their shell is broken somehow. These implants are firmer as compared to regular silicone implants and are not as likely to rupture as older silicone implant types.
How Is Breast Augmentation Done in Singapore
Before Breast Augmentation
- Assessment
A thorough examination is to be performed to better understand patients’ goals regarding their breast augmentation. Other physical examinations like breast assessment for lumps checking and history taking are the most crucial steps to perform before the surgery.
- Visualization
The patient is provided with visuals of their desired breast implants and size. This allows them to visualize their desired breast enhancement and gives them a much better understanding and idea.
- Preparations
This involves taking some necessary mammograms and ultrasounds. The patient is provided with a list of medications and precautionary measures that are needed to be avoided before the surgery.
The above steps enlisted are significant as they eliminate many obstacles and problems that are likely to occur during the surgery. This is why it is important to assess them carefully.
During Breast Augmentation
- Anesthesia
The surgery is performed by giving the patient general anaesthesia. The type of anaesthesia is decided after a proper talk between the surgeon with the patient.
- Incisions
Incisions are made depending upon the type of implant and the insertion.
- Implant Insertion
The implant is inserted depending upon the type and kind of implants and the size of breast implants. Generally, the implant is inserted either within the breast tissues or behind the pectoral muscles (breasts muscles).
- Insertion Closing
After careful insertion of implants, the incisions are closed. A list of precautions is given to the patient to take better care of the incision site. A surgical bra is later given for comfort and to ease the incision site.
After Breast Augmentation
Post-operative soreness, bruising and swelling usually resolve after a few weeks. The scars heal in approximately 6 weeks after the surgery and will continue to fade in months to come.
Recovery After Breast Augmentation Surgery
This stage is no doubt the most important yet sensitive. The patient has to be cautious to avoid the risk of infection and inflammation. For the first month of recovery, heavy activities and picking of heavy objects are not allowed. This period is a complete restring period as one misstep can cause damage to the incisions. After 4 weeks, the patient can start wearing their regular bra. Light exercises and jogging are allowed during this period.
During the recovery period, the patient has to go for check-ups for incision monitoring. Other important guidelines that need to be followed are:
- Eat healthier
- Take your medications properly
- Avoid sleeping on the implants
- Avoid putting any such pressure on the implants.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) about Breast Augmentation
Should I Wait To Have A Breast Augmentation Until After Childbirth?
This is purely a personal decision. No one can tell you that this specific time is “right” or “wrong” for you to have a breast augmentation. Breast augmentation does not affect the ability to breastfeed your baby. However, doctors do warn about a minimal risk that this procedure may decrease the sensations and interfere with the feeding reflexes essential for breastfeeding.
With age, both augmented and non-augmented breasts will experience some form of sagging and often lose volume due to breastfeeding and hormonal changes secondary to childbirth.
Can I Breastfeed After Breast Augmentation Surgery?
Studies and post-surgical trials after breast augmentation surgery have not identified any challenge related to breastfeeding. The clinical trials have shown that there is no danger of silicone breast implant materials being passed into the breast milk and affecting your child’s health.
Breast implants are typically inserted through various incision sites, such as under the breast, around the areola, or in the armpit. While these incisions might disrupt some milk ducts or nerves, many remain intact, allowing for milk production and breastfeeding.
Although some women may experience temporary changes like decreased milk production, these are often transient and may not hinder breastfeeding.
Women planning to breastfeed after breast augmentation should discuss their intentions with their plastic surgeons to ensure optimal surgical techniques for breastfeeding outcomes.
Will Breast Implants Interfere With A Mammography?
Patients with breast implants placed sub-glandularly (above the pectoralis muscle) are more prone to have interference with their mammograms. However, most surgeons greatly reduce this obstruction by placing the implant behind the pectoralis muscle (sub-muscular). You should ask your surgeon for sub-muscular implant to avoid future interference with a mammography.
When Can I Return To Normal Physical Activities After Breast Augmentation Surgery?
The breast augmentation procedure is quite safe and you can return to everyday activities within four or five days after surgery. Any swelling, pain, and discomfort can be reduced by taking medications prescribed by your doctor and following appropriate recovery and aftercare. There is no limitation on taking showers after the procedure and you will have to return to the doctor’s office for stitch removal within a week.
Most patients with breast implants return to office work after a week. Those with tough jobs that require heavy weight lifting, pushing, or stretching are advised to take a rest of at least 3 weeks and let the breast tissue heal. Sub-muscular implants take longer to be symptom-free and you may experience mild pain and a little discomfort for an additional week or two.
Most doctors advise returning to light physical activity and exercise after a week. Strenuous activities – such as push ups, bench presses, and weight lifting – that cause stretching of the chest muscles must be avoided for at least a month.
Will I Have A Dressing On After Breast Augmentation And When Can I Wear An Underwire Bra?
In most of the cases, doctors apply dressing over the small incision area along with a surgical bra to lift the breast and avoid stretching. You may be advised to wear a special bra to put pressure on the upper edge of the breast and to hold it in a lower position. The process of adjustment of a new implant may take several weeks to months. During this time period, you may have to wear unwired bras or sports bras as advised by your doctor.
The bra of your choice will be applicable after the newly implanted implant is in a good position, usually from the fourth week onwards.
What Breast Implant Size Should I Get?
It depends on several factors, including;
- Your general health
- Your individual frame
- Your appearance goals
- Previous medical or surgical conditions
The same size implant may look different from patient to patient – according to their built and shape. Your doctor will carefully choose the size and type of implant to fit your appearance goals.
Are Scars From A Breast Augmentation Noticeable?
Breast augmentation from a qualified and experienced breast surgeon will leave you with a short and well-hidden scar underneath your breast creases. They may take 6 months to a year to gradually fade and blend into the surrounding skin.
Only complex procedures such as breast lift – that require a big incision (from the base of the breast to the nipple) will have a noticeable scar mark. However, these too can be easily covered up by a bra or a bathing suit top.
What Is The Difference Between Sub-Muscular (Putting Implants “Under” The Muscle) Sub-Glandular (“Over” The Muscle) Implant?
The two most common methods used for breast augmentation include;
- Placing the implant under the pectoralis muscle (sub-muscular)
- Placing the implant between chest muscle and breast tissue (sub-glandular)
Sub-muscular implantation is the most common method used by breast surgeons to reduce post-surgical complications and provide a more natural shape to the breast. It also helps to smooth out the skin sagging and improve the breast contour. Screening for breast cancer and mammograms are easier in the sub-muscular implantation than sub-glandular.
Sub-glandular implantation involves placement of implant close to the skin – above the pectoralis muscle. This option is especially effective for women who want a more “full” and “round” appearance. It also helps correct ptotic breast or “sagging” more quickly than sub-muscular implant. However, it may hinder with breast cancer screening and mammography. Furthermore, it is also linked to a post-surgical condition called “capsular contracture” – in which hardening of the implant occurs due to scarring of the surrounding breast tissue. People with capsular contracture may need additional surgery to remove the scarring and place a new implant.
Sub-glandular implants are more noticeable than sub-muscular ones as they are placed close to the skin. In case of insufficient breast tissue, a patient may feel the edges of the sub-glandular implant.
Do My Breast Implants Need To Be Replaced Every 10 Years?
Breast implants are generally guaranteed to be durable for 10 years but it does not mean that you need to change them once the clock strikes. Replacement is usually recommended when the breast implant has ruptured.
Women can also replace the implants if they want to change the size or shape of their breasts.
As far as rupture rate is concerned, the following are estimates:
- 10 % at 10 years
- 30 % at 20 years
- 75 % at 30 years
How Much Does Breast Augmentation Cost?
Breast augmentation costs in Singapore depend on many factors like the technique, implant brand, surgery duration, and the surgeon. The more experienced the surgeon is, the more the cost is going to be. But your health and wellness should always be your priority.
Go for such a surgeon whose health center is MOH approved and is well-experienced and professional. Breast augmentation price in Singapore ranges from about $15000 to $22000. This cost included everything like the implants, surgeon’s fee, surgery, medication, and facilities.
Risks & Complications of Breast Implants
Following complications are likely to occur after breast augmentation surgery:
- Pain in breasts
- Infection
- Implant rejection
- Bleeding
- Accumulation of fluid within breasts tissues
These complications are not common but can occur if precautions are not taken seriously. Therefore, take plenty of rest and eat healthy to avoid the risk of any such complications.
