Pregnancy heralds a transformative period in a woman’s life, often accompanied by various physical changes, including those affecting the skin. A prevalent skin concern during this time is melasma, commonly known as the “mask of pregnancy.”
This article aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of pregnancy-related melasma, including its causes, management strategies, and treatment options, with a focus on pigmentation laser treatment in Singapore post-pregnancy.
Understanding Pregnancy-Related Melasma
Pregnancy-related melasma is a skin condition characterized by the development of dark, irregularly shaped patches on the face, typically on the forehead, cheeks, nose, and upper lip. These patches are usually brown or grayish-brown in color and are more noticeable when exposed to sunlight. Melasma is a common occurrence during pregnancy, and while it doesn’t pose any health risks, it can be a source of frustration for many expectant mothers.
Causes of Pregnancy-Related Melasma
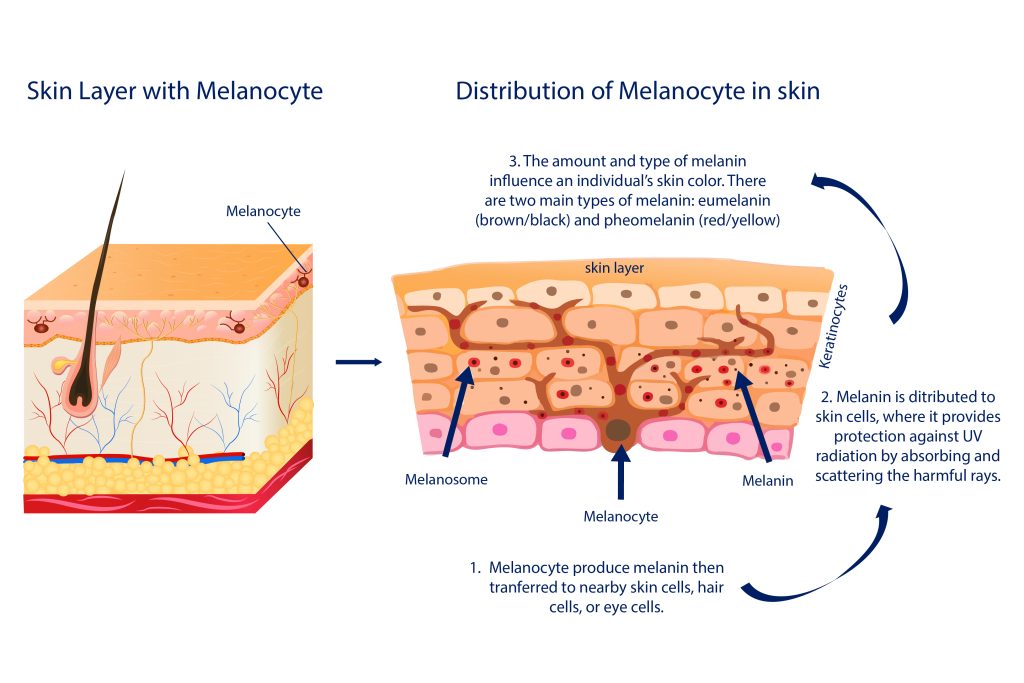
The exact cause of melasma during pregnancy is not fully understood, but it is believed to be related to hormonal changes. Pregnancy is a time when the body undergoes significant hormonal fluctuations, and these changes can impact various aspects of a woman’s physiology, including her skin. Hormones, particularly estrogen and progesterone, play a crucial role in stimulating the melanocytes, which are the pigment-producing cells in the skin. When these melanocytes become overactive, it can lead to an increased production of melanin, the pigment responsible for the color of our skin.
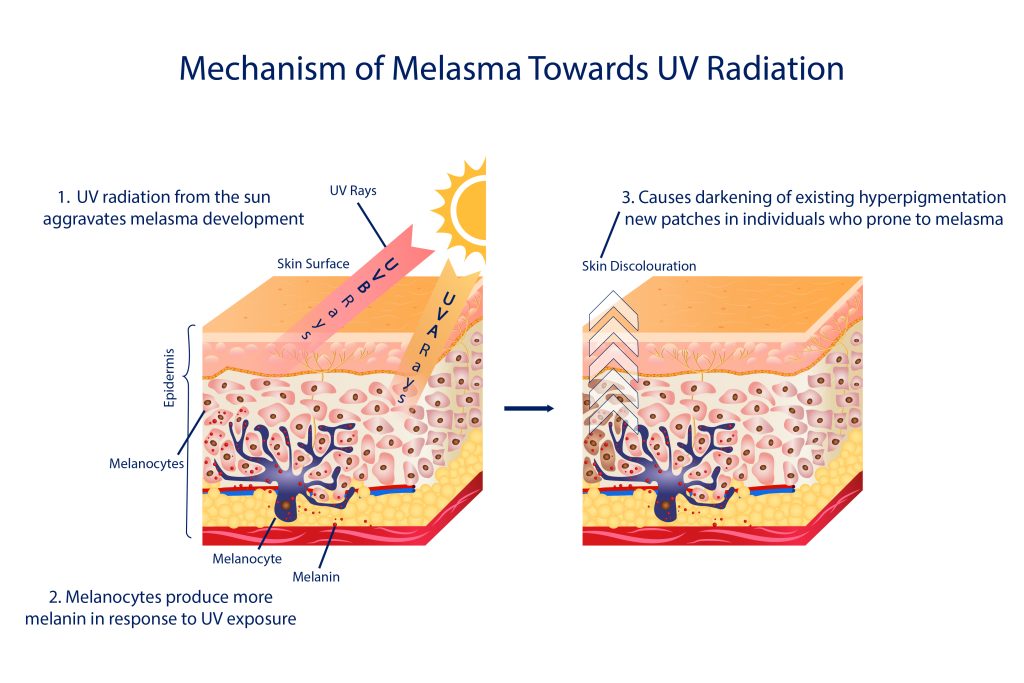
Furthermore, exposure to ultraviolet (UV) rays from the sun can exacerbate melasma. Sunlight is known to trigger the melanocytes to produce more melanin, and since melasma patches are more noticeable in areas exposed to sunlight, it is essential to take extra precautions when outdoors.
Coping with Pregnancy-Related Melasma
While melasma can be a frustrating condition to deal with during pregnancy, there are several strategies that expectant mothers can employ to cope with it effectively. These strategies focus on sun protection, wearing protective clothing, adopting a gentle skincare routine, and considering pigmentation laser treatment after pregnancy.
1. Sun Protection: Implementing rigorous sun protection is vital. Use a broad-spectrum sunscreen with high SPF, ensuring coverage against UVA and UVB rays. Reapply every two hours when outdoors and complement sunscreen use with wide-brimmed hats and sunglasses for added facial protection.
2. Protective Clothing: Opt for clothing that covers the skin, such as long-sleeved shirts, to minimize direct sun exposure. Lightweight and breathable fabrics are advisable for comfort during pregnancy.
3. Gentle Skincare: Select skincare products suitable for sensitive skin. Avoid harsh exfoliants or irritants. Use a mild cleanser, moisturizer, and hypoallergenic makeup, and ensure thorough yet gentle cleansing to prevent aggravation of melasma.
4. Pigmentation Laser Treatment After Pregnancy: For more persistent cases, pigmentation laser treatment can be considered post-pregnancy. This non-invasive procedure uses targeted laser energy to reduce melanin in affected areas, improving the appearance of melasma. However, it’s advisable to defer this treatment until after childbirth.
When considering pigmentation laser treatment, it’s essential to consult with a certified doctor. In Singapore, for example, you can find licensed clinics that offer treatments like pigmentation laser treatment. They can provide a thorough assessment of your condition and guide you through the treatment process, ensuring it is safe and effective.
Treatment for Melasma: A Technical Explanation
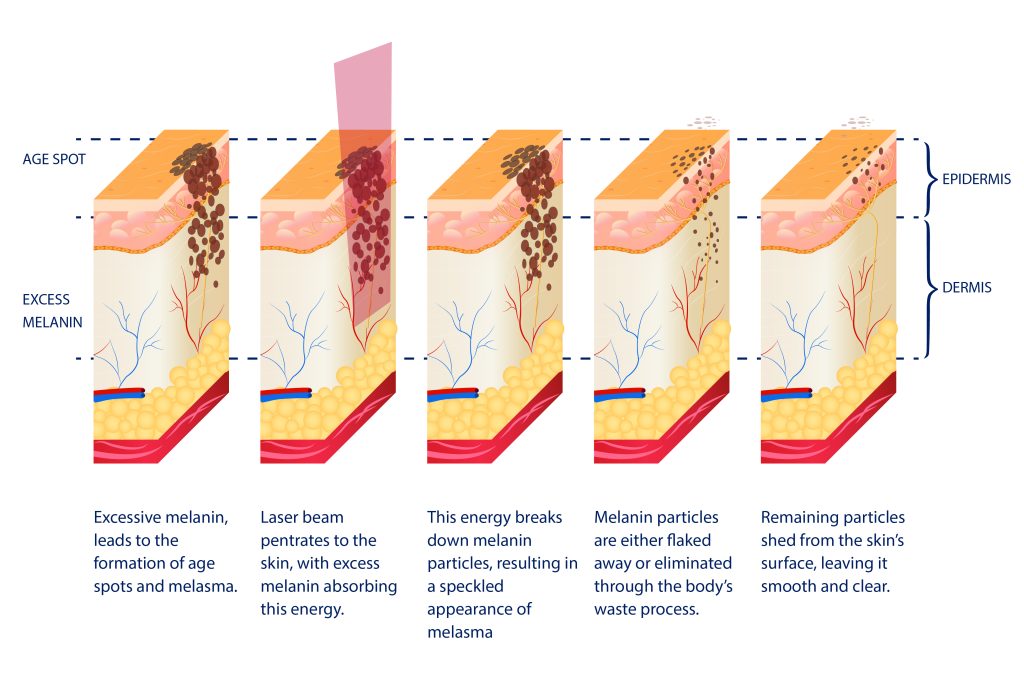
Melasma is a dermatological condition characterized by the development of hyperpigmented patches on the skin, primarily on the face. Melasma treatment often involves laser therapy, which relies on the principles of selective photothermolysis and pigment-specific targeting.
1. Selective Photothermolysis: Laser treatment operates on the concept of selective photothermolysis, where specific wavelengths of light are absorbed by the target pigment (melanin) in the skin. This absorption causes the melanin to heat up, leading to its fragmentation without significant damage to surrounding tissues. In the case of melasma, the excess melanin responsible for the dark patches is precisely targeted.
2. Wavelength Selection: The choice of laser wavelength is crucial in melasma treatment. Typically, Q-switched lasers, which emit short pulses of high-energy light, are preferred. These lasers have wavelengths that are absorbed specifically by melanin, minimizing the risk of collateral damage to nearby structures.
3. Melanin Disruption: Once the laser energy is absorbed by melanin, it leads to the generation of heat within the pigment granules. This heat disrupts the melanin particles, causing them to break down into smaller fragments. These smaller fragments are then gradually absorbed and eliminated by the body’s natural processes.
4. Optical Energy Density: The success of laser treatment for melasma depends on carefully calibrating the laser settings, including the energy density or fluence. The appropriate energy density ensures efficient melanin fragmentation while preventing excessive heating of the skin, which could result in adverse effects.
5. Post-Treatment Response: After a laser session, patients may experience some immediate darkening of the melasma patches, which is a common and expected response. Over the subsequent days and weeks, the fragmented melanin is gradually cleared by the body, leading to a lightening of the treated areas.
Alternative Melasma Treatment Options:
While laser treatment is an effective approach for melasma, it is not the only option. Certified doctors may consider several alternatives based on the patient’s skin type, melasma severity, and individual preferences. Some other treatment modalities include: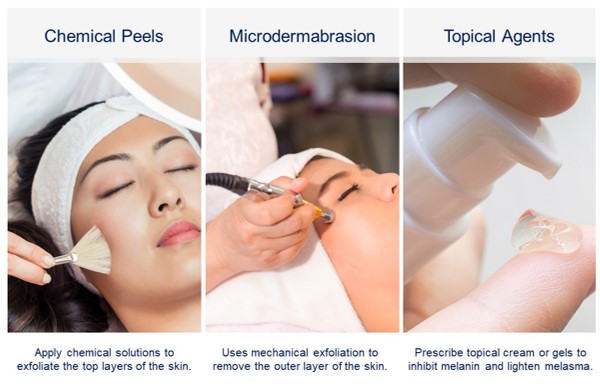
1. Chemical Peels: Chemical peels involve the application of specific chemical solutions to exfoliate the top layers of the skin, reducing hyperpigmentation and encouraging skin rejuvenation.
2. Microdermabrasion: This procedure uses mechanical exfoliation to remove the outer layer of skin, improving the appearance of melasma over time.
3. Topical Agents: The doctor may prescribe topical creams or gels containing ingredients like hydroquinone, retinoids, corticosteroids, or kojic acid to inhibit melanin production and lighten melasma.
4. Combination Therapies: Often, a combination of treatments is employed to achieve the best results. Doctors may recommend a tailored approach, incorporating laser treatment, topical agents, and other modalities to address melasma comprehensively.
It is essential to consult a board-certified doctor for a thorough evaluation and personalized treatment plan, as the choice of treatment should be based on individual factors and a thorough understanding of the patient’s unique condition.
Bottomline
Pregnancy-related melasma, often referred to as the “mask of pregnancy,” is a common concern for expectant mothers. While the exact cause of melasma is not fully understood, it is believed to be related to hormonal changes and sun exposure. Coping with melasma during pregnancy involves sun protection, wearing protective clothing, adopting a gentle skincare routine, and considering advanced treatments like pigmentation laser treatment after giving birth.
Pregnancy-related melasma may be a temporary skin condition, but it can be managed and treated effectively with the right strategies and the guidance of skilled professionals in the field of dermatology. By adopting proactive measures for sun protection and exploring treatment options, pregnant women can navigate this period with confidence, maintaining comfort and self-assurance in their skin.