
Are you also tired of hiding those discolored patches under layers of foundation? Well, you might be suffering from a skin condition called melasma. This is a skin condition characterized by freckle-like spots or blue-gray or brown patches. It is also referred to as “mask of pregnancy”.
Melasma is not a subtle condition. People with melasma are often on the look-out for the most convenient yet effective solution for this condition.
Learn how we can help you treat melasma.
What Is Melasma?
Melasma, also commonly referred to as “black spot,” is one of the most prevalent skin disorders. It primarily affects individuals between the ages of 20 and 40, with an increased risk for pregnant women and those with darker skin tones.
Melasma appears as freckle-like spots or flat patches of brown or blue-gray pigmentation. It results from increased melanin production by the cells responsible for skin color. This condition typically occurs in areas exposed to direct sunlight, such as the forearms, neck, and face — especially on the cheeks, chin, forehead, and upper lip.
Due to its frequent occurrence during pregnancy, melasma is sometimes called the “mask of pregnancy.” Although harmless and often fading over time, it can significantly affect a person’s mental well-being due to the noticeable changes in appearance.
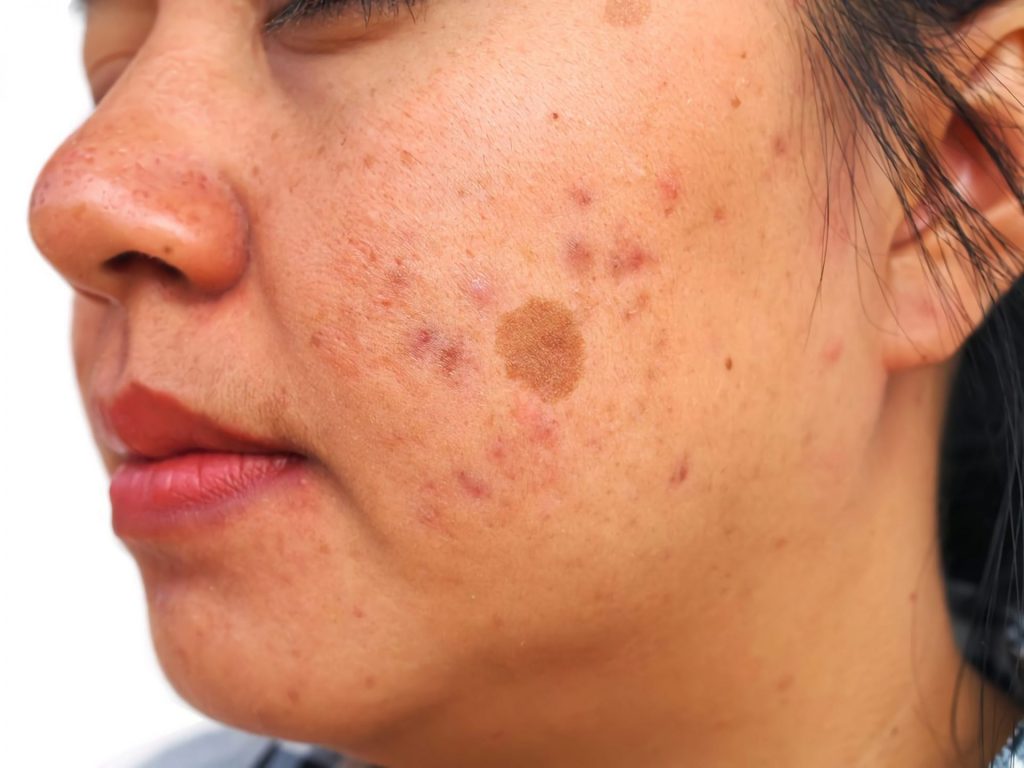
Due to increased prevalence during pregnancy, it is also sometimes termed as the “mask of pregnancy.” Though it is completely harmless and may also fade over time, it dramatically impacts the person’s mental health as their appearance changes drastically.
What Causes Melasma?
Melasma occurs due to an overproduction of melanin, the pigment that gives skin its color. Various factors contribute to this condition, including prolonged exposure to ultraviolet (UV) rays, hormonal changes, and genetic predisposition. UV radiation stimulates melanocytes, the cells responsible for pigment production, leading to visible discoloration on the skin.
Hormonal fluctuations, such as those during pregnancy or from oral contraceptives, are also common triggers. Additionally, individuals with a family history of melasma or those with darker skin types are more prone to developing this condition.
These are a few of the factors that play a crucial role in speeding the process of skin-aging:
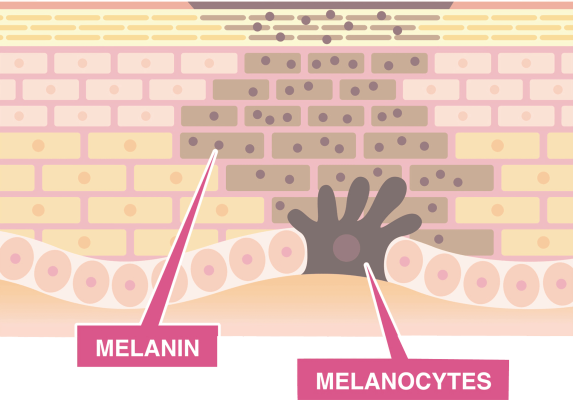
Hyperactivity of Melanocytes
Melanocytes are pigment-producing skin cells that are stimulated by the UV radiations present in the sunlight. Increased activity of the melanocytes due to sun exposure, the quantity of melanin also surges, thus giving a darker color to an area of skin.
Increase in the Abnormal Vasculature
The vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) has a direct impact on the process of melanin production. It also affects the vascular endothelial cells resulting in the release of cytokines and growth factors, causing an increase in blood vessels in the affected area.
Increased number of Senescent Fibroblasts
Fibroblasts contribute towards the increased release of melanogenic factors. In a melasmic lesion, a greater number of old fibroblasts cells are observed in the upper dermis.
Defective Basement Membrane
Melasma patients have increased metalloproteinase 2 (MPP-2), which damages the basement membrane and affects the melanocytes.
Symptoms of Melasma
Melasma is characterised by patches of discoloration that are darker than the natural skin tone. These patches are often symmetrical, appearing on both sides of the face. In some cases, melasma may also develop in other sun-exposed areas of the body.
Melasma can appear on the:
- Forehead
- Bridge of the nose
- Cheeks
- Upper lip
- Chin
- Neck
- Forearms
Unlike other skin conditions, melasma does not cause itching, pain, or discomfort, but it can impact self-esteem and confidence. If left untreated, melasma may progress to form larger, more prominent patches.
Types of Melasma
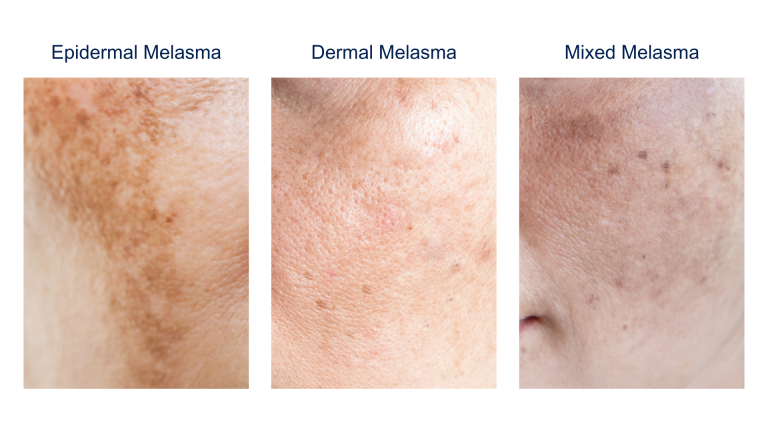
- Epidermal Melasma: This type involves pigmentation in the outermost layer of the skin and appears as well-defined, brown patches. It often responds well to treatment.
- Dermal Melasma: Pigmentation occurs in the deeper layers of the skin, resulting in bluish-gray patches that are more challenging to treat.
- Mixed Melasma: A combination of both epidermal and dermal melasma, this is the most common type, with varied coloration and responsiveness to treatment.
Melasma Treatment in Singapore
When dealing with melasma, no single treatment approach is known to offer the best results. Experts prefer a combination approach that is fine-tuned according to the severity of the melasma, the type of melasma, and your skin type.
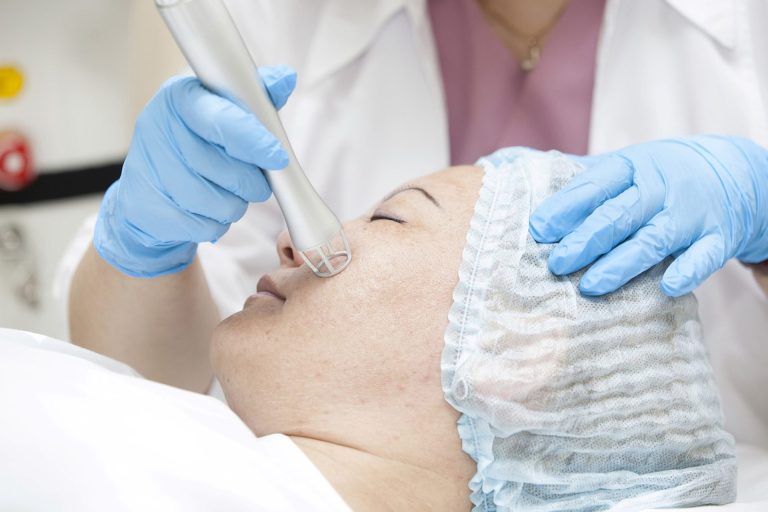
Melasma Treatments Include :
Chemical Peels: Chemical peels involve the application of specific chemical solutions to exfoliate the top layers of the skin, reducing hyperpigmentation and encouraging skin rejuvenation.
Microdermabrasion: This procedure uses mechanical exfoliation to remove the outer layer of skin, improving the appearance of melasma over time.
Topical Agents: The doctor may prescribe topical creams or gels containing ingredients like hydroquinone, retinoids, corticosteroids, or kojic acid to inhibit melanin production and lighten melasma.
Combination Therapies: Often, a combination of treatments is employed to achieve the best results. Doctors may recommend a tailored approach, incorporating laser treatment, topical agents, and other modalities to address melasma comprehensively.
Laser: Laser therapy targets the melanin in the affected areas, breaking it down into smaller particles that the body can naturally eliminate. Modern laser technologies provide precise treatment for pigmentation while minimising the risk of affecting surrounding skin, making it a reliable option for managing melasma.
Topicals Lightening Agents
Topical anti-aging products such as retinol, exfoliating hydroxy acids, and antioxidants that can help in improving skin health and delaying the signs of skin aging in general.
Skin experts emphasize that such formulas can benefit everyone, especially those patients who are suffering from melasma, but it is imperative to introduce them into your daily skincare routine gradually from a lower dose. As a result, this allows the skin tissue to avoid irritation by gradually acclimating itself.
On the other hand, prescribed topical products, which include light steroids (reduce inflammation) and hydroquinone (block pigment synthesis in the skin), can help people with melasma.
It is recommended to use these products for short periods of a few months, followed by intervals or treatment breaks.
In-clinic Treatments To Treat Melasma
In-clinic treatments can be useful and helpful for treating melasma, but the first line of defense should always be topical treatments, even though these may require a while to show results. It is important to be patient when dealing with a pigmentary condition like melasma, as it takes time to see results.
Patients with melasma want healthier, clearer, younger-looking skin. With a good pre-treatment assessment, they can get the correct treatment that is customized to their case and help minimize potential risks and disappointments.
Before looking at in-clinic treatments, you can first fine-tune your personal anti-aging home-based skincare for the long term. Your doctor can help review your home care, and ensure that it contains proper products in each category, such as anti-oxidants, retinol, acids, hydration, and sunscreen.
From there, the professionals will recommend items best suited to your skin type while guiding you through the proper use to help ensure correct application.
In some instances, doctors recommend and supervise the use of prescription products that include steroid formulations and specialized hydroquinone.
However, there may be a few people who might not tolerate such products because of skin sensitivities. In this case, in-clinic procedures can be considered, particularly when some pigment synthesis procedures cannot be targeted by tablets or creams. These include laser-based treatments, chemical peels, and radio frequency micro needling.
Light-based treatments such as IPL and lasers have long been used to treat existing pigment in the skin tissue and minimize the new pigment synthesis to help achieve quick results.
That said, it is critical to observe caution when treating melasma with such procedures because overzealous energy use sometimes causes skin irritation and worsens the condition.
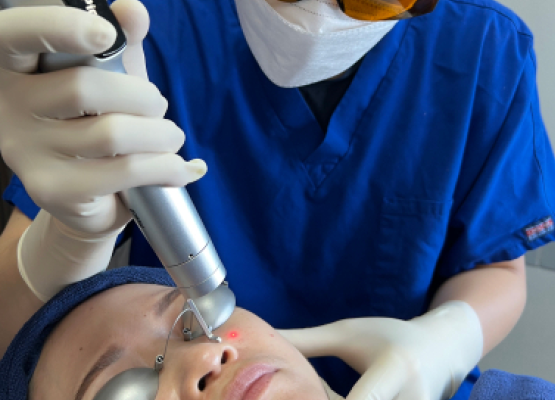
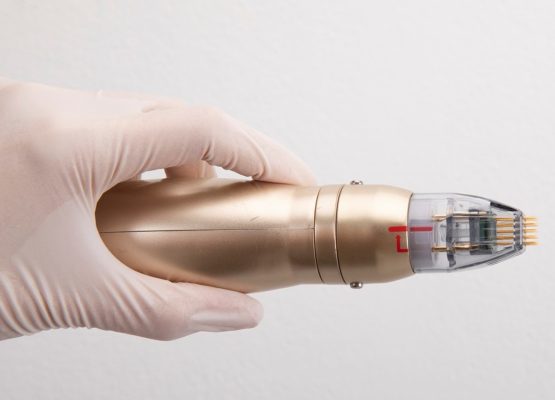
While laser-based treatments focus primarily on pigment and the cell structures that synthesize them, radiofrequency microneedling procedures are geared towards normalizing inflamed blood vessels and restoring healthy and clear skin.
These procedures can sometimes create transient micro-channels for administering anti-pigment and anti-oxidant topical products.
It is imperative to be cautious when considering oral prescription treatments (tranexamic acid tablets). It should only be considered for the short term and with the full supervision by a doctor.
How To Prevent Melasma
Preventing melasma involves adopting habits that protect the skin from potential triggers:
- Use Sunscreen Daily
Regular application of broad-spectrum sunscreen with high SPF can shield the skin from harmful UV rays, which exacerbate melasma.
- Wear Protective Clothing
Hats, sunglasses, and UV-blocking apparel reduce direct sun exposure.
- Avoid Prolonged Sun Exposure:
Limiting time under direct sunlight, especially during peak hours, can help minimise risk.
- Be Cautious with Hormonal Treatments
If possible, discuss alternative options with a healthcare provider to manage hormonal fluctuations.
- Maintain a Healthy Skincare Routine
Using non-irritating products and avoiding harsh treatments can prevent aggravation of melasma-prone skin.
Frequently Asked Questions About Melasma Treatment
The number of sessions varies based on the severity of melasma and the chosen treatment method. Typically, noticeable improvements can be observed after 4–6 sessions, but this may differ for each patient.
Most treatments are minimally invasive and cause little to no discomfort. Some patients may experience mild redness or sensitivity, which typically subsides quickly.
While treatments can effectively reduce pigmentation, melasma may recur due to triggers such as sun exposure or hormonal changes. Consistent preventive measures are crucial.
Yes, many treatment options are suitable for various skin types and can be customised to address specific skin concerns. A consultation with a qualified medical doctor is essential to assess your skin condition and recommend the most appropriate treatment plan.
Downtime varies depending on the procedure. Most treatments involve minimal recovery time, allowing patients to resume daily activities shortly afterward.
